Feature Focus: How to use Github Actions to scan your applications with CAST Highlight
How it works
The CAST Highlight action has three main elements:
- The action script (action.yml) which contains the different steps, the events that will trigger the action and the scope (e.g. branches) of the action on the repository
- Some environment variables attached to your repository which contain CAST Highlight identifiers for the application
- A secret variable at the repository level which contains your user authentication token
Let’s see the content of an action in detail to learn how to customize it for your needs.
In our Github Action that you can download from the marketplace, the CAST Highlight scan is scheduled to happen twice a month, the typical duration of a development sprint.
name: CAST Highlight Scan
on:
schedule:
- cron: 0 6 1,15 * *
Here, we define a trigger to run the action based on a scheduled cron expression. The action will be performed at minute 0 of 6th hour (6am), on 1st and 15th days of the month. This website can help you with writing your cron if you’re not familiar with this syntax: https://crontab.guru/#0_6_5,15_*_*
Github Actions support other triggers like manual launch (workflow_dispatch) or based on specific events like push or pull requests. You can find all configurable events available from this page: https://docs.github.com/en/actions/reference/events-that-trigger-workflows#example-workflow-configuration
The next section of the script is dedicated to dynamically provision a Docker container running on Github and check out your repository to run the CAST Highlight scan.
jobs:
scan:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
environment: prod
Github offers Github-hosted runners in various operating systems (see the list here), depending on your needs. In our case, we use Linux Ubuntu to run the command line.
Then, we add a step that will perform a checkout on the repository. We use a ready-to-go action from the action marketplace called Checkout (https://github.com/marketplace/actions/checkout).
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
The next step is about getting CAST Highlight variables that the command line will use to automatically upload scan results to the right application on the CAST Highlight portal.
- name: get company and application ids
run: |
cat .github/workflows/hl.env >> $GITHUB_ENV
These variable need to be listed in an hl.env file you will add to your repository in the “.github/workflows” folder.
Finally, the last step is about passing information to the Docker image of the CAST Highlight command line as follows:
- name: scan project source code
run: |
docker run --rm -v $(pwd):/s -v /tmp:/w casthighlight/cli \
--sourceDir /s \
--workingDir /w \
--tokenAuth ${{ secrets.CAST_HIGHLIGHT_API_TOKEN }} \
--companyId ${{ env.companyId }} \
--applicationId ${{ env.applicationId }} \
--serverUrl ${{ env.serverUrl }}
If you’re familiar with the CAST Highlight command line interface and/or the Docker image of the command line, you’ll see the common CAST Highlight options for specifying the scan and upload options.
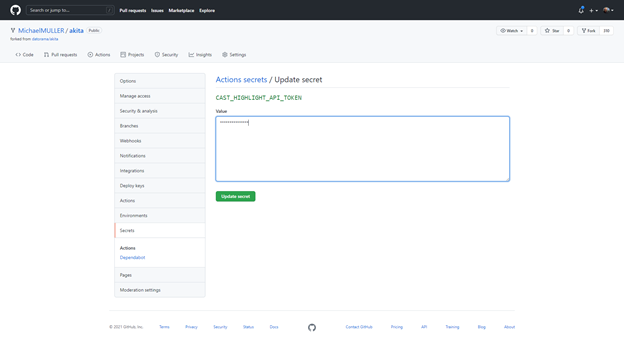
As soon as a scan job is run, you can monitor how it’s going through the action logs as shown below.